The researchers compared a typical 6mg dose of the steroid dexamethasone to a 12mg dose in patients who needed more help maintaining their oxygen levels.
It’s the first COVID-19 experiment to report long-term mortality, and it’s one of the few that was ‘blinded,’ or constructed in such a manner that doctors couldn’t tell which patients got which dose.
Higher Dosages Of Corticosteroids May Be Beneficial To Covid Patient
While a larger dose of steroids did not significantly reduce mortality in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19, there was a trend toward benefit without additional side effects, according to a major international trial.
As per the known variants of coronavirus, it affects the lungs first. The pores of the lungs are filled with infection, and hence the capacity of the same is reduced to a great extent as far as intake of oxygen is concerned.
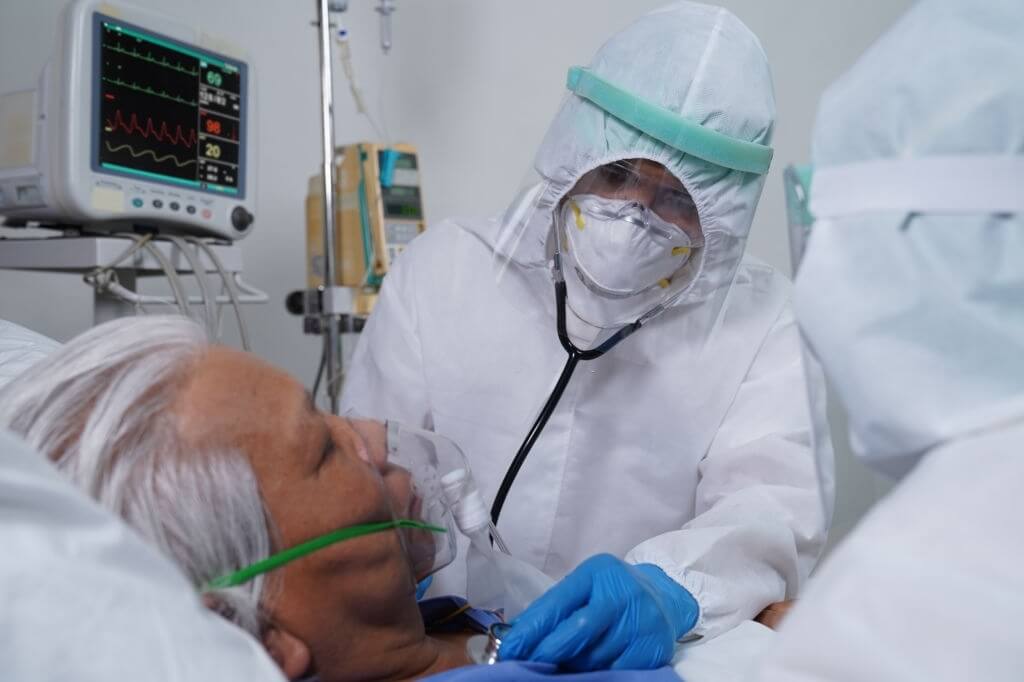
This leads to a lower oxygen level in the blood, and as a result, the body feels a lack of the required level of oxygen in almost all organs.
The lack of oxygen can turn into multi-organ failure that leads to fatality. However, as per a few experts, this situation can be countered with the help of corticosteroids that can keep the infection under check.
Although prior research revealed that higher doses of dexamethasone might benefit individuals with more severe COVID-19, there had been worries about potential side responses, according to study co-author Professor Bala Venkatesh of The George Institute for Global Health.
“There were no variations in the frequency of adverse events between the two doses in our trial. While infections with the so-called “black fungus” have been reported in COVID-19 patients with a weaker immune system, our research observed no rise in infection rates with greater steroid doses “, he stated.
Patients with serious COVID-19 generally have significant lung inflammation and low oxygen levels, necessitating increased oxygen support, mechanical ventilation, blood pressure support, and renal dialysis. The mainstay of treatment for severe COVID-19 is dexamethasone.
While a daily dose of 6 mg is advised for up to ten days, some evidence suggests that a greater dose may benefit patients with more severe conditions. The suppression of the immune system, which reduces the body’s ability to fight various forms of infections, is a potential side effect of steroid use.
Some COVID-19 patients treated with steroids have developed deadly fungal infections known as mucormycosis or “black fungus.”Between August 2020 and May 2021, researchers recruited 1000 adult patients with proven SARS-CoV-2 infection from 31 sites in 26 hospitals in Denmark, India, Sweden, and Switzerland.
The patients were divided into two groups, one getting 12 mg dexamethasone intravenously (n=503) and the other receiving 6 mg dexamethasone daily (n=497) for up to 10 days. After 28 days, 42.6 percent of patients in the 12mg group were alive and did not require life support, compared to 40.2 percent in the 6mg group.
The death rates in the 12mg and 6mg groups were 27.1 percent and 32.3 percent, respectively. Professor Vivek Jha, who set up and ran the experiment in the 12 participating hospitals in India alongside Prof Venkatesh, said the study provided important guidance to clinicians treating COVID-19 patients around the world.
“While the findings do not show that dexamethasone 12 mg is superior to 6 mg, we did see a trend toward less need for life support and mortality at the higher dose without an increase in the risk of major infections,” he said.
“Because dexamethasone is inexpensive, readily available, and indicated for the treatment of COVID-19 patients with critically low oxygen levels, even a small difference in death rates or health outcomes could result in significant clinical and health-economic benefits at the population level,” says the study.