Cancer bacteria must be capable of avoiding being attacked by the participant’s immunological systems, in addition, to growing into a serious tumor.
That’s why immunotherapy, which aids the immune response in detecting and fighting tumors, has become such an essential therapeutic option for people with cancer.
New Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Biomarker Discovered
A group of experts has described the FDA-approved circuit inhibitor immunotherapeutic and their modes of activity in this study.
It is a fact that the virus of Corona affects the lungs first. The infection is spread in the lungs, which reduces the capacity of the same, and over a few days, the patient feels trouble with breathing that leads to fatality.
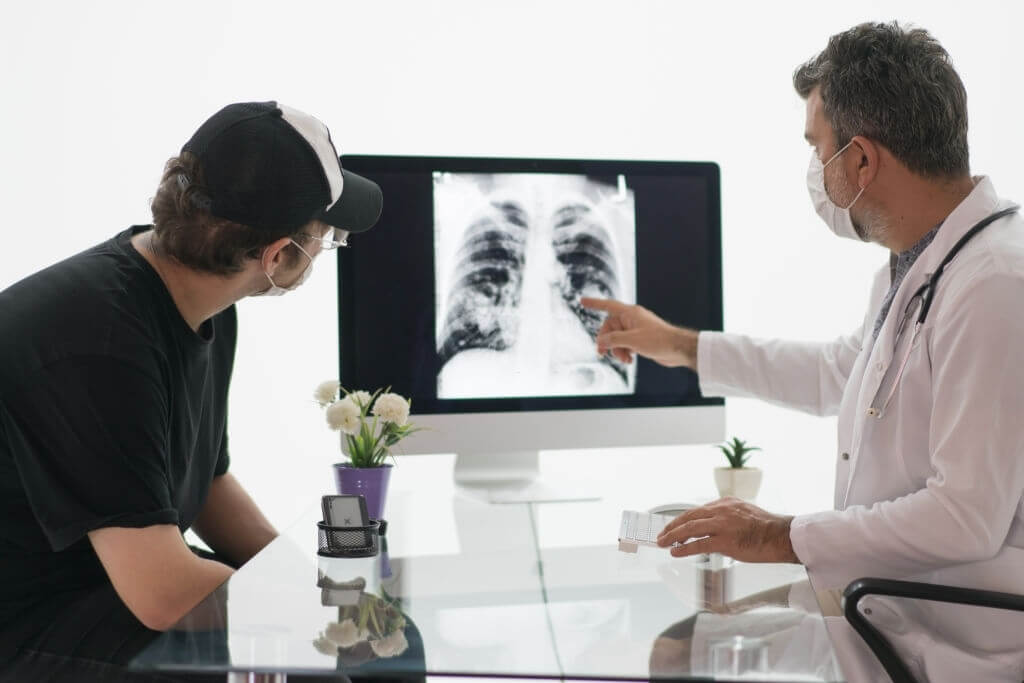
To avoid such infection, it is required that the lungs are saved from the spread of infection, and this can be done with the help of effective immunotherapy.
Having an emphasis on biomarkers of metastatic disease, NSCLC, and ‘cancerous invariant’ biomarker, we reviewed significant data in main research released in the past five years, revealing possible measures indicative of therapeutic recovery. We describe the two major types of possible markers, genetic profiles, and proteome signature, in general.
Nevertheless, predicting whether individuals may respond with such treatments has proven tricky. Researchers have made a stride towards better immunotherapy tailoring. The iCAN scientists discovered a novel diagnostic, deactivated AMPK, in a report reported in Clinical Cancer Research (lo-P-AMPK). It might be used to assess how effectively the body reacts to lung cancer immunotherapy.
After alterations in the tumor inhibitor LKB1, iCAN scientists discovered that the AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK) associated antigen display apparatus operates as facilitators of the tumor’s capacity to remain under the immunity program’s screen.
“We observed a clear correlation between lo-P-AMPK and suppressed anti-tumor immunity in lung cancer patients – even in the absence of LKB1 mutations,” comments M.Sc. PekkaPäivinen, a doctoral student involved in the study.
Providing insight into how malignant tumors can evade immunotherapeutic. Immunological escape, or the capacity to escape the host’s immune reaction, has been related only to a handful of particular genetic alterations in cancerous cells.
The tumor inhibitor LKB1 is one significant example. Lung malignancies with LKB1 mutation react to monoclonal antibodies even poorly than the lung tumors lacking abnormalities. As a result, there is a lot of curiosity about how LKB1 polymorphisms affect therapy.
The human-to-human relationships are confirmed in a lung physical model wherein AMPK removal resulted in the immunological escape & defective signal transduction. In a lung cancer physical model, a novel biomarker has been confirmed.
The research additionally proposed a novel biomarker for human immune prediction. Lower concentrations of phosphorylated AMPK (lo-P-AMPK) were found to correspond to low numbers of T-cells in pulmonary adenocarcinoma patients.
“Developing this lung cancer model enabled us to provide a direct genetic approach to demonstrate the link between LKB1, AMPK, and antigen presentation. The international collaboration with the Viollet and Verschuren labs was critical in achieving these results,” notes Dr. Yan Yan, the corresponding author of the study.
When future iCAN trials confirm lo-P-AMPK as a diagnostic in lung carcinoma therapy, the novel instrument may aid people directly by predicting who is most prone to help from monoclonal antibodies.
Even though several prospective markers have indeed been identified, the FDA has only authorized 3 tests (one as a partner diagnosis and 2 as a supplementary diagnostic) to detect individuals who were almost certain to respond with anti-PD1/PDL1 therapy.
We talked about how integrative techniques like deep genomics, transcriptomics, & deep learning are helping to identify and validate biomarkers.
A variety of investigations have discovered combos of proteome indicators that, while not always prognostic of an immune reaction when used alone, are highly linked to predicted mortality if used together.