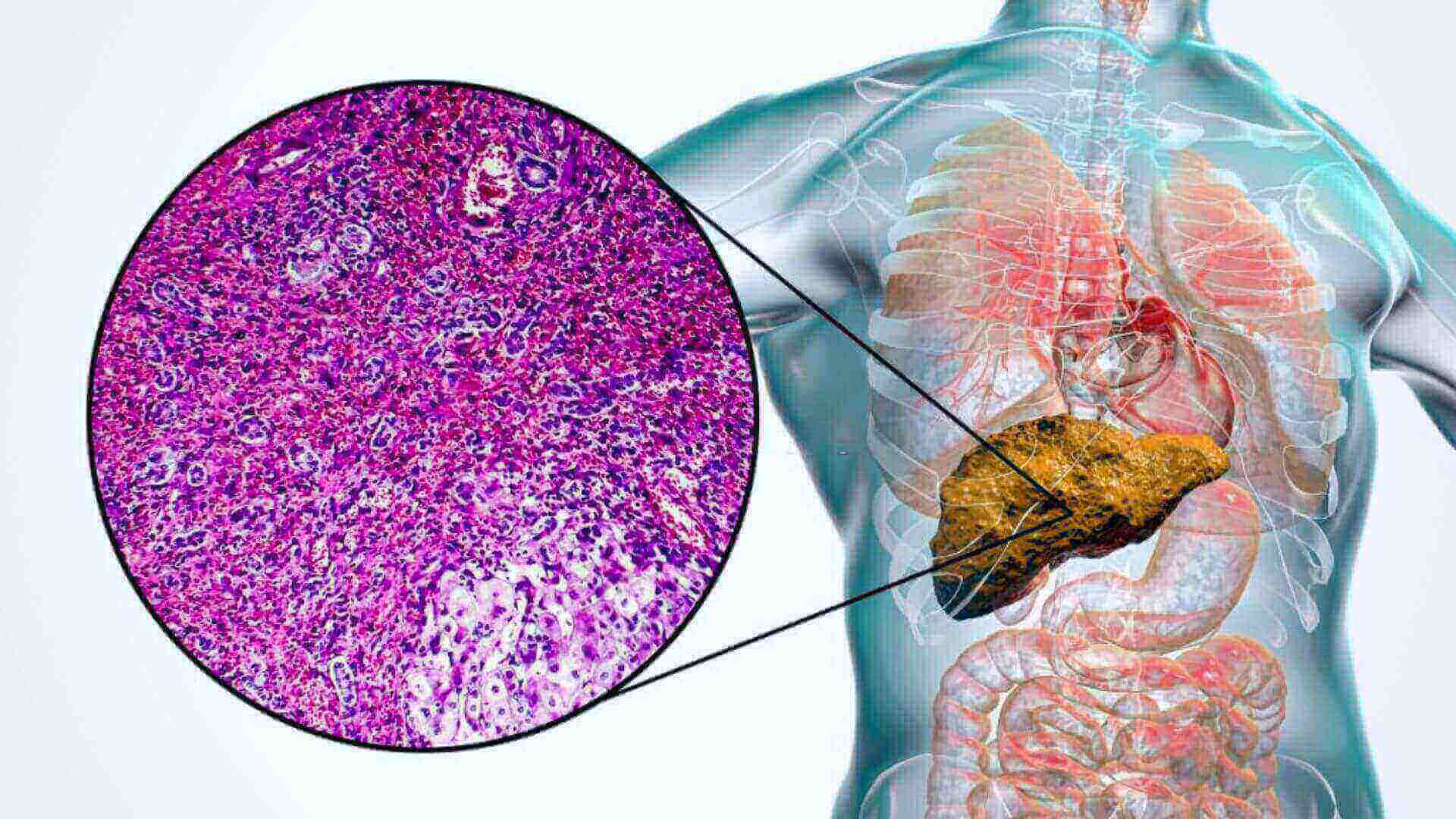
Cirrhosis is characterized by fibro and nodular development in the liver as a result of a persistent injury that disrupts the liver’s natural lobular arrangement. Viral infections poison genetic disorders, and inflammatory processes are just some of the things that can harm the liver.
Laboratory Test Trusted by Many Physicians Can Overlook Liver Cirrhosis
The liver generates damaged tissue (fibrosis) in response to each insult, but it does so without compromising its function at first. Almost all of the hepatocytes fibrosis after long-term damage result in loss of functioning and the formation of cirrhosis.
The establishment of hypertension and hemodynamic flow is the leading source of illness and death in cirrhotic individuals. Portal hypertensive arises as a result of intrahepatic and systemic scarring and vast regulatory alterations resulting in the creation of vascular supply and hemodynamic bloodstream.
The reverse impact occurs in the system and splanchnic circulation, including increased NO production leading to the system and renal pelvis dilatation and reduced vascular resistance. This causes the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) to become activated, resulting in salt and water accumulation and hyperdynamic circulation.
Therefore, in cirrhosis with hypertension, there is a portal vein deficiency of vasodilators (mostly NO) but an extramedullary excess of NO in the splenic and supply chain execution resulting in sinus vascular constriction and splenic (systemic) dilatation. By enhancing venous return, the components also assist in hyperdynamic circulation.
Taxonomy of Morphology
Cirrhosis can be micronodular to ensure this happens or mixed in appearance. This categorization is less relevant in therapeutic settings than the etiology category.
Cirrhosis caused by alcohol hemolytic anemia, hepatic venous outflow blockage, chronic bile obstruction area of at least bypass, and Indian childhood cirrhosis are all examples of the presence of different concentrations of cirrhosis.
- Macronodular cirrhosis caused by hepatitis C virus alpha-1 antitrypsin deficit and primary biliary cholangitis): Cirrhosis caused by hepatitis C virus alpha-1 antitrypsin deficit and biliary cholangitis.
- Mixed cirrhosis where micronodular & macronodular cirrhosis traits are present: Micronodular cirrhosis usually evolves to entire moving cirrhosis over time.
“These patients would have severe disease and sequelae, but their liver tests would appear to be normal. So, if you just looked at their liver tests, you’d think they were fine but that wasn’t the case,” Rockey stated.
Based on to if their cirrhosis is medically balanced or moderate to severe, patients having cirrhosis might be silent or symptomatic. Patients with compensated cirrhosis are frequently asymptomatic, and their condition is discovered by chance by blood tests, physical examination, or imaging.
Mild to moderate elevations in transaminases or gamma-glutamyl phosphodiesterase with potential enlarged liver and spleen on the exam are usual results.
Decompensated cirrhosis, on the other hand, is associated with a wide variety of signs and symptoms resulting from a mix of liver impairment and portal hypertension. When a person with cirrhosis develops edema, hepatitis, liver encephalopathy, variceal hemorrhage, or hepatocellular cancer, the patient has progressed from a balanced to a liver cirrhosis stage of the disease.
In patients with ascites, further cirrhosis consequences include bacteremia sepsis and kidney dysfunction. The liver is permanently damaged. However, further harm to the liver must be prevented to slow the disease’s course. Avoiding alcohol being vaccinated against HBV and HCV, eating a well-balanced diet losing weight, and treating parts to create like hydration hypertension and infection early help prevent liver disease.
Regular positive of volume status renal function varies formation and progress to HCC is used to achieve this.
Antiviral drugs in viral hepatitis steroids and immunosuppressive agents in rheumatic diseases usnic acid and people acid in biliary cholangitis copper chelating agents in Ewing sarcoma and iron chelating agents and phlebotomy in iron overload are some of the treatments available.
In NASH, losing a weight of at minimum 7% is advantageous, and abstinence from alcohol is essential in alcoholic liver disease.