The coronavirus pandemic has posed a severe threat to mankind, in terms of human loss as well as economic loss. The devastation brought by it is immeasurable. It has affected all classes of society, people from all age groups. Masking, social distancing, sanitizing, and periodic shutdowns have become the new norms of society now. The unvaccinated people and the vaccinated people are getting infected with coronavirus and its multiple strains.
Diagnostic Tests For Coronavirus, PCR, and Rapid Antigen Tests
An infected individual can spread the disease to others unless proper measures like masking, isolation, etc., are not taken. So the preliminary step to stop the spread of the infection is getting tested for the infection. The standard diagnostic tests for getting tested for coronavirus are RT-PCR and rapid antigen tests, the treating physician makes the final decision for which testing to be done.
RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction), also called molecular test, detects the presence of virus in a laboratory setting. Fluid samples are collected from the back of the nose (nasopharyngeal swab) or the back of the throat (oropharyngeal swab). The collected specimens are then sent to a laboratory, where the collected genetic material is amplified. RT-PCR is a highly accurate test that can detect even the smallest amount of coronavirus particles in the sample. Hence it is regarded as the standard method for diagnosing coronavirus infection.
Employees returning to work after testing positive for Covid-19 or who have a recent travel history either within the country or outside the country are asked to provide a negative RT-PCR report by their employers.
But RT-PCR tests have their own disadvantages also. Firstly it is costly compared to the rapid antigen tests. Secondly, it needs a skilled technician and specialized pieces of equipment like PCR heating machines, so it can be done only in specialized laboratory settings. It may take several hours to days to get the final results. In a few cases, PCR tests may give positive results even after the infected person has recovered fully from the infection or is no longer infected. This is because the PCR picks up the small fragment and amplifies this small fragment, giving a positive result. Says Dr. Leana Wen, an emergency physician and visiting professor of health policy and management at the George Washington University Milken Institute School of Public Health, that PCR tests are not reliable after a few days of getting infected.
The best time to do a PCR test is when a person starts to experience the symptoms or has come in close contact with anyone already infected with the coronavirus.
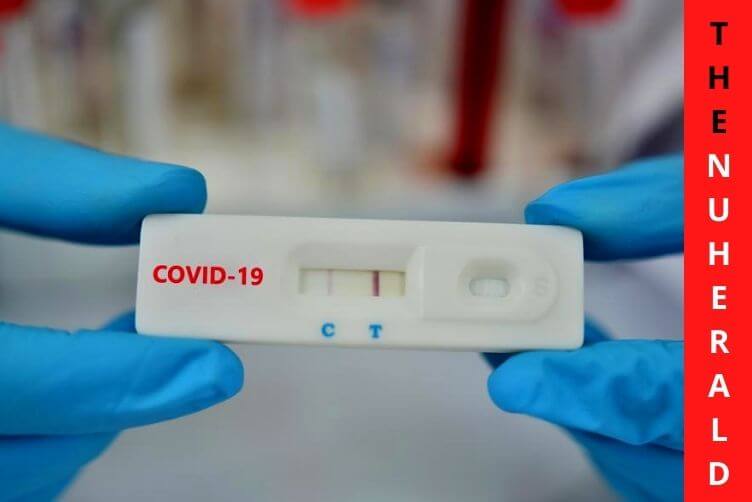
On the other hand, rapid antigen tests are much cheaper, much faster, though the results may not be accurate. Antigens are substances that cause antibodies to form. For a rapid antigen test, the sample is first treated with a liquid and then this liquid is then applied on a test strip with several chemicals.
The advantages of these rapid antigen tests are they are easy to perform, can be done in a home setting, and the results are quicker. Rapid antigen tests are beneficial to confirm if a person infected with Covid-19 for many days is no longer infectious to other persons. If a rapid antigen test turns out to be negative, the person can stop isolating but mandatorily use a mask. Having negative rapid antigen tests for consecutive 2 days indicates the person is no longer contagious. These tests pick up viruses only when there is high viral overload, so the results may not always be accurate.
The diagnostic testing for coronavirus may include one or more testing, depending on the symptoms, recent exposure, travel history, and healthcare professionals’ decision. But as soon as one starts experiencing any symptoms, isolating from others is the first step to prevent the spread of infection.